The TubaVent®-catheter – a new treatment for in-ear pressure
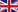
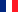
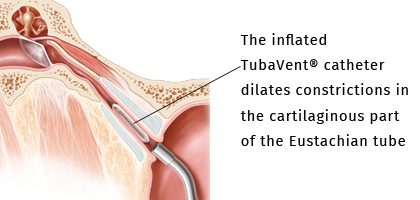
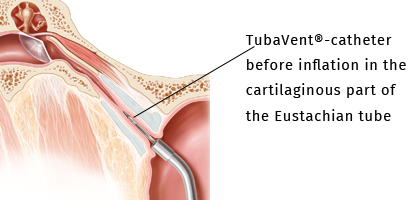
Balloon dilatation of the Eustachian tube is a new method for treating Eustachian tube dysfunction. Your ENT consultant will refer you to a specialist clinic for this minimally-invasive procedure. Under a short-acting anaesthetic, a balloon is used to dilate the patients Eustachian tube: to do so, the surgeon inserts a balloon catheter through the nose and into the cartilaginous part of the Eustachian tube.
The balloon is then inflated to create pressure of 10 bar over a period of two minutes. This results in dilation of the constrictions in the tube. This dilation restores proper tube function, enabling both normal air exchange and the pressure equalisation procedure.
For a large proportion of the many patients treated worldwide, this procedure will lead to a significant reduction in symptoms within about two months after the operation. Your ENT consultant will decide whether this treatment method is appropriate for you. If so, your doctor will refer you to your local ENT clinic.
Tube training for post-operative success
 As a balloon dilation aftercare procedure, we advise you to regularly train the ventilation of the Eustachian tubes. A suitable training method is the "Valsalva manoeuvre". Pinch your nostrils together and then, keeping your mouth shut and while tensing your stomach muscles, breathe out as if you were blowing your nose. This manoeuvre works to equalise pressure in the ears while also opening the Eustachian tubes. Ask your doctor how many times a day you should conduct the Valsalva manoeuvre as a post-operation procedure. Experience suggests about 3–5 times a day.
As a balloon dilation aftercare procedure, we advise you to regularly train the ventilation of the Eustachian tubes. A suitable training method is the "Valsalva manoeuvre". Pinch your nostrils together and then, keeping your mouth shut and while tensing your stomach muscles, breathe out as if you were blowing your nose. This manoeuvre works to equalise pressure in the ears while also opening the Eustachian tubes. Ask your doctor how many times a day you should conduct the Valsalva manoeuvre as a post-operation procedure. Experience suggests about 3–5 times a day.
For full details on the TubaVent®-catheter, please download our ![]() printable patient information leaflet.
printable patient information leaflet.